“According to Gartner’s report, the global public cloud services was supposed to generate 411.4 billion dollars by 2020.”
It indicates that worldwide businesses are adopting cloud services at a steady rate to tackle all business operations. Cloud computing offers an extensive, flexible, and affordable way to implement cloud service models. The leading players of the IT sector compete to deliver flexible cloud services for the public and enterprises. Since cloud services have already shown exponential growth around the world over many years. Thus, you must adapt your business to fit in the cloud model and leverage wider possibilities of cloud service models (such as IaaS, SaaS, PaaS, CaaS, and FaaS) to bring the flexibility and efficiency for pushing your business growth. However, keep in mind that if this technology is underutilized, your business can lag.
In this blog post, we will walk through various cloud service models that will help you identify which cloud model you should deploy into your business infrastructure.
IaaS
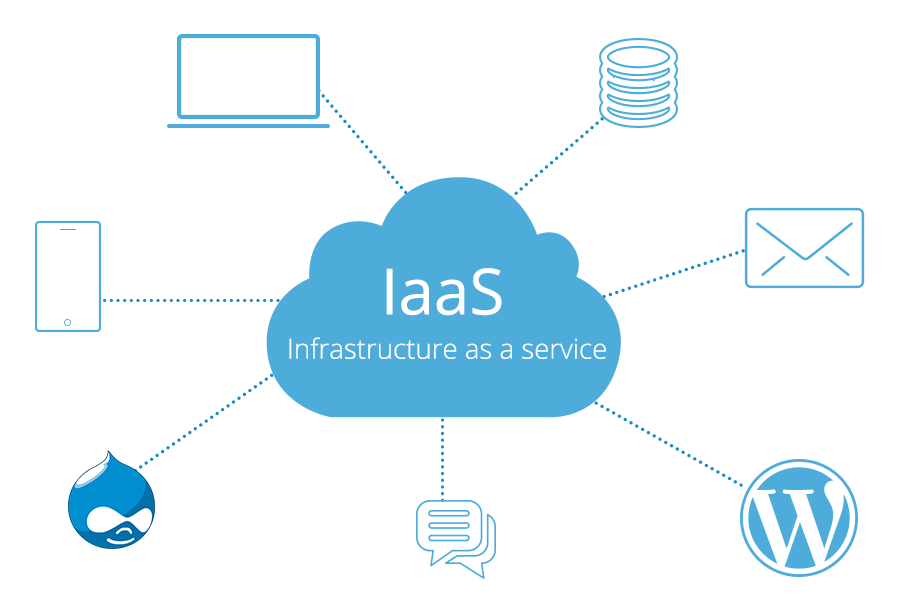
IaaS refers to Infrastructure as a Service. Using the services of IaaS (like Amazon EC2), a company can use compute servers or instances on-demand. In short, the hardware and software stack up to the operating system is managed for you. Further, you will require to choose which operating system to use with your instance (Windows or Linux). Also, you will be responsible for the configuration and management of the operating system and any software that you install on it.
An API is usually provided for all cloud services, which can be utilized for programmatic management. Each compute instance will have an allocated storage capacity and cloud networking functions such as firewalls, routing, and load balancers that can be configured.
The market size of IaaS was worth 38.94 billion U.S. dollars in 2019 and expected to grow up to 201.83 billion U.S. dollars by 2027. Microsoft Azure IaaS, Amazon EC2, Google Compute Cloud, and Rackspace are some of the IaaS services.
Advantages of IaaS
- No need to invest in your hardware.
- The infrastructure scales on-demand to support dynamic workloads.
- Increase stability, reliability, and supportability.
- Maintain operational control of the operating system.
SaaS
SaaS refers to Software as a Service. This service model delivers software applications over the internet. SaaS services do not require any coding, so it is ready to use in the consumer space, such as Facebook and Gmail.
SaaS manages the entire stack, but you will have some limited scope to configure the service based on your requirements.
The present worth of the SaaS market was estimated to be 104.7 billion U.S. dollars. Google Apps and Microsoft Office 365 are examples of SaaS services.
Advantages of SaaS
- Sign up and rapidly start using an innovative business app.
- Apps, as well as data, can be accessed from any connected computer.
- No data loss in case your computer breaks, as data is in the cloud.
- The service can be dynamically scaled to usage needs.
PaaS

PaaS refers to the Platform as a Service. It removes the complexity of developers and operational overhead from them. The cloud service provider uses PaaS to manage the infrastructure layer, development tools, middleware, database management systems, business intelligence (BI) services, and much more.
It enables developers to concentrate on their code without the requirement of managing the environment in which it runs. Developers can upload their code to build web applications. PaaS supports building, testing, deploying, managing, and updating the web application.
With PaaS, you are not only limited to web services, the PaaS platform as a service model also offers databases. The service provider takes care of the management of the database engine and underlying hardware, and you can create tables and add data. For instance, database PaaS offers Microsoft Azure SQL and Amazon RDS.
At present, 20% of the overall cloud services market comprises PaaS and expected to reach almost 60 billion U.S. dollars by 2022. Microsoft Azure, IBM PaaS, and Google Cloud Platform are the major players in PaaS.
Advantages of PaaS
- Reduce coding time – develop applications faster
- Deploy new web applications to the cloud in less time (minutes)
- Minimize complexity with middleware as a service
CaaS
CaaS refers to the Container as a Service. It provides service between IaaS and PaaS, based on the implementation. Using the CaaS service, the cloud service provider manages the container engine for you. For instance, Docker. You can upload, organize, run, scale, manage, and stop containers using a management console or API.
The CaaS market was estimated to increase from 930.4 million U.S. dollars in 2017 up to 4080.4 million U.S. dollars by 2022 at a CAGR of 34.4%. AWS Elastic Container Service, Google Container Engine, Microsoft Azure Container Service are examples of CaaS services.
Advantages of CaaS
- Pay only for what you use (like load balancing and compute instances).
- You can easily scale up a container.
- Due to the support and management of the provider, CaaS services are responsive, secure, and stable.
- It helps developers streamline the process of building a scaled-out container and application deployment.
FaaS
FaaS refers to the Functions as a Service. It is a part of a suite of services called serverless services. Using serverless architecture, you do not require to worry about launching, managing, or scaling any compute resources such as server instances, clusters, or load balancers.
Serverless computing is also known as microservices applications. In FaaS, compute processes are presented as functions. You need to upload your code that runs when a request is received. When no request is received, no cost is incurred due to the serverless behavior of functions.
AWS Lambda, Google Functions, and Microsoft Azure Functions are examples of FaaS services.
Advantages of FaaS
- The cloud service provider handles all server management. Therefore, no need for developers.
- No need to pay for idle resources.
- Built-in availability and fault tolerance.
- Functions scale automatically and independently.
- Less management overhead. It means more time to focus on coding.
In The End
We suggest you quickly adopt a cloud platform for your business so that you can leverage its wide-reaching benefits, and as a consequence, grow your business. You must carefully choose the cloud model that is apt for your business requirements and also delivers the desired result. If you are still unable to identify which cloud model is the best solution for your business, then contact the GrayCell experts at +91-7307242527 or email at info@graycelltech.com and clear your confusion.